CRYPTO CAPITAL GAINS
Are you investing in cryptocurrency? Remember, crypto capital gains taxes – understanding them can save you from a headache and potential penalties in the future!
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Gains from cryptocurrency selling are considered capital gains and are subject to taxation.
- The holding duration and purchase price heavily influence the computation of crypto capital gains.
- A greater tax rate applies to capital gains realized over a shorter period than those held longer.
- Tax-loss harvesting, giving, donating, and tax-advantaged accounts may all be used to reduce crypto capital gains tax.
- Cryptocurrency investors should know foreign tax laws and regulations, such as the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA).
- Accurate reporting of crypto capital gains on tax returns is essential to prevent possible fines and legal concerns.
- Staying current on tax laws and regulations is vital to staying compliant and maximizing financial planning in the cryptocurrency industry.
INTRODUCTION
The rising value of cryptocurrency may be attributed to the growing popularity of this kind of digital money. The obligation of understanding tax ramifications, however, comes with every investment. Therefore, the fundamentals of crypto capital gains and their importance in the cryptocurrency market will be covered in this guide.
Profit made from the selling of cryptocurrency is called crypto capital gains. A capital gain is realized when an investor receives more money from the sale of cryptocurrency than they initially invested in the asset. The gains are subject to taxation, the rate of which is determined by several factors, including the length of time the asset was held and the initial cost of the asset.
Because it influences their taxable income, understanding crypto capital gains is essential for cryptocurrency investors. Severe fines and legal troubles may result from a failure to comply with tax regulations. Therefore, it is vital to correctly disclose capital gains on tax returns to prevent such issues.
Investors may improve their financial planning by better understanding crypto capital gains. In addition, it may help them decide the best time to acquire or sell cryptocurrency, minimizing any capital gains tax they may owe.
This guide will cover all aspects of crypto capital gains that investors should be aware of. The definition of capital gains and its cryptocurrency application will be covered first. The factors influencing crypto capital gains, such as the acquisition price and the holding term, will also be explored.
The guide will also cover calculating cryptocurrency capital gains, including establishing the cryptocurrency’s cost basis and reporting cryptocurrency gains and losses on tax returns. Strategies, including tax-loss harvesting, gifting, and using tax-advantaged accounts, will also be outlined, all to minimize crypto capital gains.
The tax ramifications for cryptocurrency investors will also be covered in the guide. In addition, it will cover FATCA compliance rules for overseas accounts and how international transactions affect tax liability.
To sum up, cryptocurrency investors need to have a thorough understanding of crypto capital gains. It enables them to maximize their financial planning, comply with tax rules, and avoid fines. To help investors make informed judgments regarding their investments, this guide will present in-depth information on crypto capital gains.
UNDERSTANDING CRYPTO CAPITAL GAINS
Understanding how cryptocurrency affects taxes, particularly concerning capital gains, is important as more individuals engage in the technology. This portion of the article will cover the definition of capital gains and how they apply to cryptocurrency.
Gains on the sale of capital assets are referred to as capital gains. Various forms of cryptocurrency and real estate are also included in this category. An investor will realize a capital gain if they sell an asset for more than they paid.
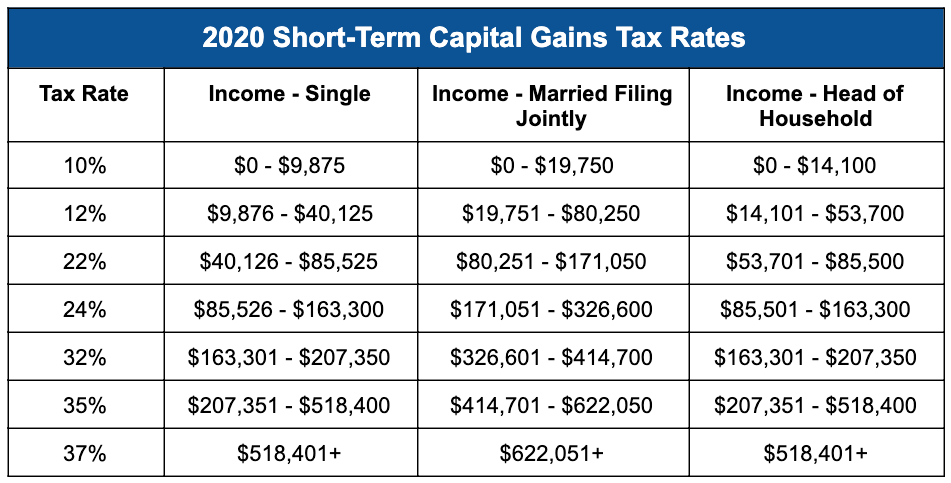
Photo:
TaxBit
Crypto capital gains apply to income gained from the sale of cryptocurrency. Gains in the capital are realized when an investor receives a higher price for their cryptocurrency upon selling than they first paid. However, it’s important to remember that an investor still has a taxable event even if they don’t convert their cryptocurrency to fiat money.
The Internal Revenue Service treats cryptocurrency as property for tax reasons. Investors in cryptocurrencies must thus record capital gains on their cryptocurrency returns. Penalties and other legal complications might occur from failing to comply with tax rules.
Assets held for less than a year are eligible for short-term capital gains. Long-term capital gains, which apply to assets held for more than a year, are taxed at a lower rate than short-term capital gains. The investor’s tax bracket determines the rate at which long-term capital gains are taxed.
The date the investor purchased the cryptocurrency and the date they sold it determines the holding period for cryptocurrency. An investor would realize a short-term capital gain, for instance, if they purchased Bitcoin in March 2021 and sold it in August 2021.
Cryptocurrency investors must understand investor capital gains. Accurately reporting capital gains on tax returns and complying with regulations are crucial for avoiding fines and legal complications. When calculating capital gains, it’s also important to understand the distinction between short-term and long-term capital gains. As a result, investors may improve their financial planning and make wise cryptocurrency investing selections.
FACTORS THAT AFFECT CRYPTO CAPITAL GAINS
Investors in cryptocurrencies should be aware of the factors influencing their capital gains. Therefore, the primary factors that affect crypto capital gains will be covered in this section.
- Cost of Acquisition
The purchase price is the amount an investor must fork out to get their hands on any cryptocurrency. The investor’s capital gains might be affected by this price. The likelihood that an investor would realize a capital gain when they sell cryptocurrency is higher if they buy it at a lower price. On the other hand, they could not realize a capital gain or might even incur a capital loss if they buy cryptocurrency at a higher price.
- Retail Value
The amount an investor gets after selling their cryptocurrency is known as its sale price. The investor’s gain or loss on capital investment will depend on this price. A cryptocurrency investor will realize a capital gain if they sell their cryptocurrency at a higher price than they purchased. Conversely, they will incur a capital loss if they sell their cryptocurrency for less than they purchased.
- Time in Holding
The holding period describes how long an investor waits to profit from selling their cryptocurrency. An investor will realize a short-term capital gain or loss if they retain their cryptocurrency for less than a year before selling it. A long-term capital gain or loss will be realized if they retain their cryptocurrency for more than a year before selling it.
- Tax Codes and Statutes
Tax rules and regulations may have a big influence on cryptocurrency capital gains. To comply with IRS regulations, investors must appropriately record capital gains on their tax filings. In addition, penalties and other legal complications might occur from failing to comply with tax rules.
- Search Terms: Cryptocurrency Price Swings, Tax Consequences, Internal Revenue Service Rules
Several factors affect crypto capital gains, including acquisition price, selling price, holding term, and tax rules and regulations. Cryptocurrency investors should be aware of these factors to maximize their financial planning and make educated investment selections. They also need to be aware of the tax consequences of their investments and the influence that cryptocurrency price volatility might have on their capital gains. This allows investors to reduce their taxable income while increasing their returns.
CALCULATING CRYPTO CAPITAL GAINS
Cryptocurrency investors must precisely calculate their capital gains to comply with tax rules and regulations. How crypto capital gains are determined is the topic of this section.
- Cryptocurrency Cost Estimation
An investor’s first purchase price of a cryptocurrency is considered its cost basis. Investors need to know the purchase price, transaction fees, and other expenditures involved with the investment to determine the cost basis. Therefore, all transactions, including the date, price, and other pertinent facts, should be recorded accurately. Users can more easily calculate capital gains on certain cryptocurrency exchanges since they supply cost-basis information.
- Gains and losses are determined
Investors may calculate their capital gains or losses after identifying their cost basis. Investors deduct their cost basis from the selling price to calculate capital gains. For example, if an investor bought one Bitcoin for $10,000 and sold it for $15,000, the investor would have a $5,000 capital gain. Conversely, a capital loss of $2,000 would result if the investor sold the same amount of Bitcoin for $8,000.
- Tax Reporting of Profits and Losses
An investor’s capital gains or losses must be reported correctly on their tax returns. To report cryptocurrency transactions, they should complete Form 8949 and include it with their tax return. On Schedule D of their tax return, investors should additionally report any capital gains or losses. You must appropriately report any capital gains or losses you experience to avoid fines and legal trouble.
- Cost Basis, Capital Gain Tax, and Tax Forms
In conclusion, investors must precisely calculate the cost basis of their cryptocurrency, report their gains or losses, and report them on their tax returns to determine cryptocurrency capital gains. In addition to complying with tax rules and regulations, investors should maintain accurate records of their transactions. They can reduce their tax burden and stay out of trouble with the law if they do this. To ensure they comply with tax rules and regulations, cryptocurrency investors should also consult a tax expert.
STRATEGIES TO MINIMIZE CRYPTO CAPITAL GAINS
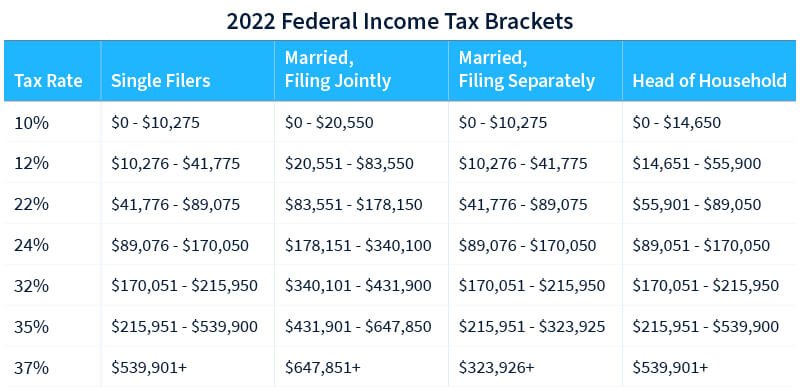
Photo:
CoinLedger
Investors in cryptocurrencies may use various strategies to minimize their capital gains taxes. The strategies that investors might use to minimize their crypto capital gains will be covered in this section.
- Harvesting Tax Deductions
A strategy known as tax-loss harvesting includes selling assets to offset capital gains from profitable ventures. Cryptocurrency investors might use this strategy to minimize capital gains taxes. For example, selling another cryptocurrency at a loss if the investor has made capital gains. This may lower their tax bill.
- Cryptocurrency Gifting
Giving cryptocurrency as a gift is another strategy investors may use to minimize their cryptocurrency capital gains. An investor may avoid paying capital gains taxes on cryptocurrency if they gift it to a close relative or friend. However, the gift receiver will be subject to taxes once they sell the cryptocurrency.
- Giving to Charity using Cryptocurrency
Investors may also contribute cryptocurrency to charity to minimize their capital gains taxes. When an investor gives cryptocurrency to a charity, the charity receives the cryptocurrency at its current market value, and the investor receives a tax deduction for the contribution. The investor will also not be subject to capital gains taxes on the cryptocurrency they contribute.
4.. Making use of tax-deferred investments
To minimize their cryptocurrency capital gains, investors may also employ tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s. Investments maintained inside these accounts are exempt from capital gains taxes, and investors may deduct their contributions from their taxable income. There are, however, restrictions on contributions and withdrawals from these accounts.
- Tax-Deferred Accounts, Tax-Loss Harvesting, and Other Tax-Avoidance Strategies
As discussed above, investors may minimize their crypto capital gains by using various strategies. Some strategies investors might use to minimize their tax burden include tax-loss harvesting, giving cryptocurrency, donating cryptocurrency to charity, and utilizing tax-advantaged accounts. It is recommended that investors seek the advice of a tax expert to formulate the most advantageous investment strategy. Tax planning is crucial for cryptocurrency investors to minimize tax bills and increase earnings.
CRYPTO AND INTERNATIONAL TAXATION
Investors need to understand the tax implications of holding cryptocurrency in various countries as the cryptocurrency sector expands internationally. Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) and cross-border transactions will also be covered along with the tax implications of holding cryptocurrency in many countries.
- Cross-Border Tax Consequences When Storing Cryptocurrency
The tax implications of holding cryptocurrency vary depending on the country, and cryptocurrencies are regarded differently in various countries. For example, while some countries see cryptocurrency as an asset or property, certain countries view it as money. Income tax, capital gains tax, value-added tax (VAT), and goods and services tax are just a few examples of the tax implications of holding cryptocurrency in various countries.
- Cryptocurrency Investors and the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA)
U.S. legislation known as the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) mandates that foreign financial institutions provide information about their customers who are residents of the United States to the IRS. For cryptocurrency investors who store their funds in foreign accounts or use foreign cryptocurrency exchanges to buy and sell cryptocurrencies, FATCA has significant implications. Significant fines may be imposed for failure to comply with FATCA.
- International Deals and Tax Consequences
Tax implications might be significant for cross-border cryptocurrency transactions. For example, when an investor buys or sells cryptocurrency across borders, they may be subject to different tax regulations in each country. When the same income is taxed twice in two distinct countries, this is called “double taxation.”
- Search Terms: International Tax, Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act, and Cross-Border Deals
In conclusion, investors should understand these tax implications since holding cryptocurrency in several countries might have significant tax implications. For cryptocurrency investors who store their funds in foreign accounts or trade on foreign exchanges, the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) has significant implications. Investors should be informed of the tax legislation in each country to prevent double taxation. In addition, cross-border transactions utilizing cryptocurrency could have significant tax implications. If investors want to be sure they are by all applicable rules and regulations, they should talk to a tax specialist with experience in international taxes.
CONCLUSION
To begin, we established a working definition for the term “capital gains” related to cryptocurrency holdings. We also discussed the tax impact of short-term and long-term capital gains.
The next topic we covered was how the purchase price, the selling price, the holding time, and the applicable tax laws and regulations all play a role in determining your crypto capital gains. Finally, we examined how tax regulations and cryptocurrency price volatility might impact your taxes.
Then, we dove into computing crypto capital gains, including establishing the cost basis of your cryptocurrency, calculating gains and losses, and reporting them on your tax returns.
Finally, we covered methods to minimize your crypto capital gains, including tax loss harvesting, cryptocurrency gifts, charity donations, and tax-advantaged accounts.
Since cryptocurrency investments are subject to ever-evolving tax laws and regulations, you must keep up with the latest developments. Substantial penalties and fines may be imposed for non-compliance with these laws.
If you’re investing money in cryptocurrency, you must know about crypto capital gains. You may minimize your tax burden and increase your investment profits by adhering to the rules mentioned in this guide and remaining current on tax laws and regulations







































Comment Template